
But some ICs, such as the 741, are available in metal cans which can be easily opened with a hacksaw. Dangerous concentrated acid is required to dissolve the epoxy package and see the die. Integrated circuit usually come in a black epoxy package. NPN transistors are highlighted in blue and PNP transistors are in red. The die photo and schematic below are interactive.Ĭlick components in the die photo or schematic to explore the chip, and a description will be displayed below. The 741, though, includes clever circuits to shut down the output before damage occurs. Many integrated circuits will overheat and self-destruct if you accidentally short circuit an output. Doing away with the external capacitor made the 741 extremely popular, either because engineers are lazy or because the reduced part count was beneficial.Īnother feature that made the 741 popular is its short-circuit protection. ĭave Fullagar had the idea to put the compensation capacitor on the 741 chip using the new manufacturing process. Op amps before the 741 required an external capacitor to prevent oscillation, which was inconvenient. The output from the differential amplifier goes to the second (gain) stage, which provides additional amplification of the signal.įinally, the output stage has large transistors to generate the high-current output, which is fed to the output pin.ĭie for the 741 op amp, showing the main functional units.Ī key innovation that led to the 741 was Fairchild's development of a new process for building capacitors on ICs using silicon nitride. The two input pins are connected to the differential amplifier, which is based on the differential pair described above. The interactive chip viewer below provides more explanation. The internal circuitry of the 741 op amp has been explained in many places, so I'll just give a brief description of the main blocks. Thus, the differential pair is a surprisingly simple circuit that routes current based on the difference in input voltages.
As one input continues to increase, more current gets pulled into that branch. If one of the input voltages is a bit higher than the other, the corresponding transistor will conduct more current, so one branch gets more current and the other branch gets less. If the input voltages are equal, the current will be split equally into the two branches (I1 and I2). The key is the current source at the top provides a fixed current I, which is split between the two input transistors. The schematic above shows a simple differential pair. If the two inputs are equal, the current is split equally. The current source sends a fixed current I through the differential pair. Schematic of a simple differential pair circuit. It turns out that transistors on a chip look nothing like this, and the base often isn't even in the middle! If you've studied electronics, you've probably seen a diagram of a NPN transistor like the one below, showing the collector (C), base (B), and emitter (E) of the transistor, The transistor is illustrated as a sandwich of P silicon in between two symmetric layers of N silicon the N-P-N layers make a NPN transistor. Transistors are the key components in a chip. The structure of the integrated circuit NPN transistors inside the IC Your cell phone uses op amps for filtering and amplifying audio signals, camera signals, and the broadcast cell signal. Op amps are all around you: your computer's power supply uses op amps for regulation. Op amps are used as amplifiers, filters, integrators, differentiators, and many other circuits. How often do you need to subtract two voltages? And why amplify by such a huge factor: will a 1 volt input result in lightning shooting from the op amp? The answer is feedback: by using a feedback signal, the output becomes a sensible value and the high amplification makes the circuit performance stable. If you've studied analog circuits, op amps will be familiar to you, but otherwise this may seem like a bizarre and pointless device.

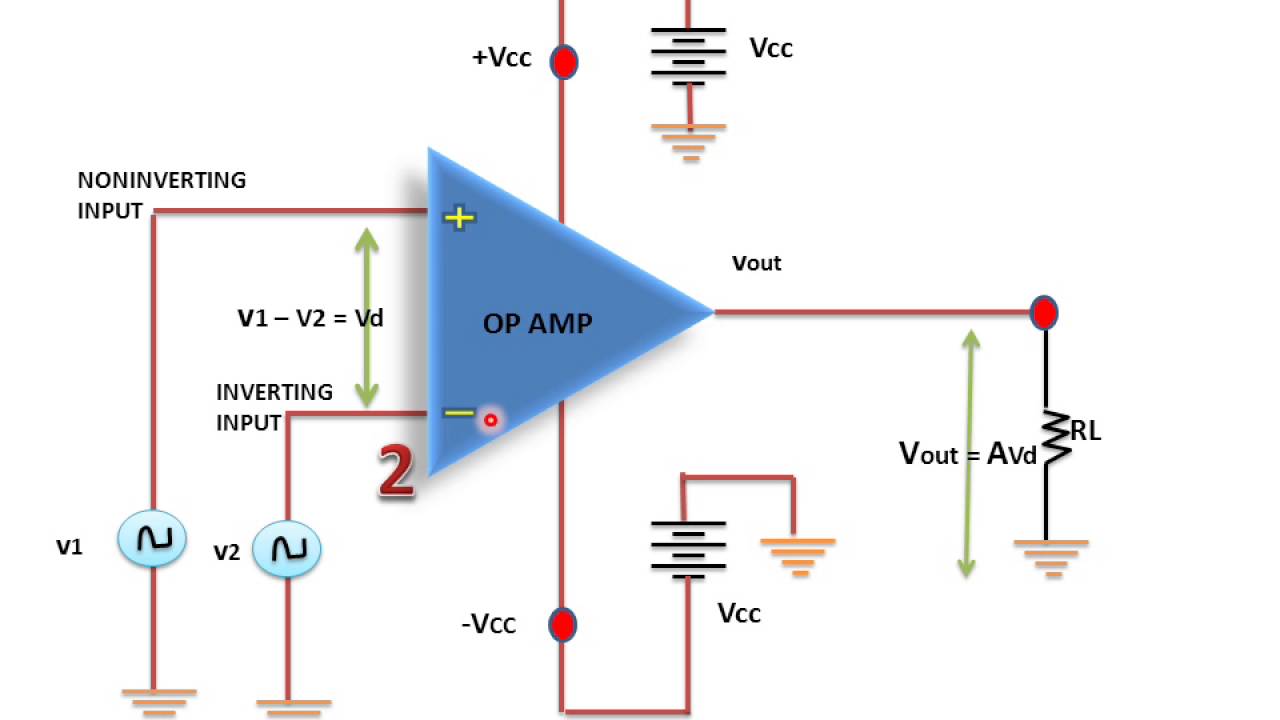
Op amps are a key component in analog circuits.Īn op amp takes two input voltages, subtracts them, multiplies the difference by a huge value (100,000 or more), and outputs the result as a voltage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
